Introduction to the Spring IoC Container and Beans
IOC容器和bean介绍
This chapter covers the Spring Framework implementation of the Inversion of Control (IoC) principle. IoC is also known as dependency injection (DI). It is a process whereby objects define their dependencies (that is, the other objects they work with) only through constructor arguments, arguments to a factory method, or properties that are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method. The container then injects those dependencies when it creates the bean. This process is fundamentally the inverse (hence the name, Inversion of Control) of the bean itself controlling the instantiation or location of its dependencies by using direct construction of classes or a mechanism such as the Service Locator pattern.
The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. The BeanFactory interface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object. ApplicationContext is a sub-interface of BeanFactory. It adds:
Easier integration with Spring’s AOP features
Message resource handling (for use in internationalization)//消息资源处理,在国际化的时候用到
Event publication //活动发布
Application-layer specific contexts such as the WebApplicationContext for use in web applications.//上下文环境
简而言之,BeanFactory提供了配置框架和基本功能,而ApplicationContext添加了更多企业特定的功能。
ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的完整超集,在本章中仅在Spring的IoC容器描述中使用。
有关使用BeanFactory而不是ApplicationContext的更多信息,请参见BeanFactory。
在Spring中,构成应用程序主干并由Spring IoC容器管理的对象称为bean。
Bean是由Spring IoC容器实例化,组装和以其他方式管理的对象。否则,bean仅仅是应用程序中许多对象之一。Bean及其之间的依赖关系反映在容器使用的配置元数据中。
//这个地方的通俗理解是bean是一个高级对象,是经过springIOC处理的,具有完整生命周期的对象
容器概述
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口表示Spring IoC容器,并负责实例化,配置和组装Bean。容器通过读取配置元数据来获取有关要实例化,配置和组装哪些对象的指令。配置元数据以XML,Java批注或Java代码表示。它使您能够表达组成应用程序的对象以及这些对象之间的丰富相互依赖关系。
Several implementations of the ApplicationContext interface are supplied with Spring. In stand-alone applications, it is common to create an instance of ClassPathXmlApplicationContext or FileSystemXmlApplicationContext. While XML has been the traditional format for defining configuration metadata, you can instruct the container to use Java annotations or code as the metadata format by providing a small amount of XML configuration to declaratively enable support for these additional metadata formats.
spring 提供了applicationContext接口的几种实现。在单应用中,通常创建的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext或者FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,尽管XML是定义配置元数据的传统格式,但是您可以通过提供少量XML配置来声明性地启用对这些其他元数据格式的支持,从而指示容器将Java注释或代码用作元数据格式。
在大多数应用场景中,实例化一个Spring IoC容器的一个或多个实例不需要显式的用户代码。例如,在Web应用程序场景中,应用程序的web.xml文件中简单的八行(约)样板Web描述符XML通常就足够了(请参阅Web应用程序的便捷ApplicationContext实例化)。如果您使用Spring Tools for Eclipse(Eclipse支持的开发环境),则只需单击几下鼠标或击键即可轻松创建此样板配置。
下图显示了Spring的工作原理的高级视图。您的应用程序类与配置元数据结合在一起,以便在创建和初始化ApplicationContext之后,您将拥有一个完全配置且可执行的系统或应用程序。
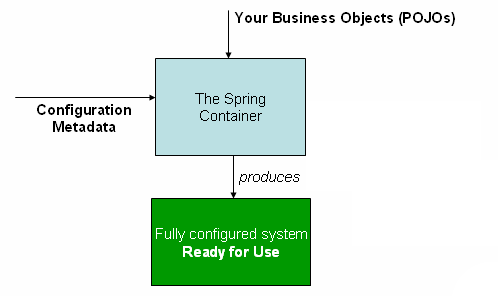
Configuration Metadata
如上图所示,Spring IoC容器使用一种形式的配置元数据。此配置元数据表示您作为应用程序开发人员如何告诉Spring容器实例化,配置和组装应用程序中的对象。传统上,配置元数据以简单直观的XML格式提供,这是本章大部分内容用来传达Spring IoC容器的关键概念和功能的内容。
配置元数据传统上是依赖于简单和直观的xml格式,这是本章大部分IOC容器用来传达关键概念和功能的形式
基于xml 的配置不是唯一的配置元数据的形式,IOC容器与实际上写入的配置元数据是解耦的。当前很多开发者选择java-based configuration配置他们的spring应用。
其他的配置元数据的形式,有如下几种:
- annotation-based configuration(基于注解形式的配置):spring2.5引入了基于注解的元数据配置
- java-based configuration:开始于spring3.0,很多基于的Spring javaConfig的功能变成了spring
框架的一部分。从而你可以通过java而不是xml文件定义你的应用程序外部的bean。比如@Configuration,@Bean,@Import和@DependsOn
spring 配置包含了最少一个bean,通常在容器里管理多个bean,基于XML的配置在定义bean的时候,在最外层使用的是
这些bean的定义相当于组成你应用的实际对象。通常,你定义了服务层的对象,DAOs,表示层对象(Strus中的Action,JMS 队列)。通常在容器中不会配置细粒度域的对象,因为创建和加载域对象是Daos和业务逻辑的职责。然而,你可以使用spring和AspectJ集成那些在IOC容器之外的被创建的对象,
1 | <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" |
实例化一个Spring容器
提供给Application Context构造函数的一个或多个位置路径是资源字符串,这些资源字符串使容器可以从各种外部资源(例如本地文件系统,Java CLASSPATH等)加载配置元数据。
1 | ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml"); |
当你学习完spring IOC容器后,你可能想要知道更多关于resource相关的内容,比如他提供了一个更方便的机制,用于从URI本地路径定义的路径中读取InputStream
1 | <bean id="petStore" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.services.PetStoreServiceImpl"> |
在上面的例子中,服务层由PetStoreServiceImpl和两个Dao组成。这个property name元素指的是java Bean属性的名称。ref元素指的是另外一个bean定义的名称。ref关联的是另外一个的id。
组成基于XML配置的元数据
跨多个xml文件来对bean进行定义可能很有用,通常来说,每个独立的 xml配置文件代表的是你体系中的逻辑层或者模块。
你可以使用application context 构造器去加载这些xml文件中的bean定义。这个构造器包含了多个resource位置。或者,使用一个或多个import标签去加载其他文件中的bean定义,如下图
1 | <beans> |
在上面的例子中,外部的bean定义从这三个文件中来:services.xml,messageSource.xml,themeSource.xml。所有位置的路径都会在导入定义文件后被关联到。在上面的配置中 ,services.xml在当前目录中,messageSource和themeSource在resource目录中,斜杠被忽略了。然而,给出的路径都是相对路径,最好不要用斜杠。被引入的文件的内容(包含了顶级的beans标签),都必须是符合spring schema规范的,合法的xml bean definitions。
备注的说明:
- 使用“../“ 路径是可行的,但是不被推荐,因为可能引入项目之外的文件。特别是,不建议将关联使用
classpath:URLs(例如:classpath:../services.xml) - 你可以使用标准的资源位置而不是相对路径的形式。使用
classpath,需要多注意的是你要讲文件放在正确的路径下面,通常要与绝对位置保持一个间接的引用,例如,使用${JAVA_HOME}来代表jvm环境变量。
命名空间自己提供了导入指令的功能。Spring所提供的一系列XML名称空间(例如,上下文和util名称空间)中提供了超出普通bean定义的其他配置功能。
groovy Bean定义的DSL
作为一个外部配置元数据的更深入的例子,bean定义可以被Groovy使用的DSL来表达,常见的用于Grails框架中,通常,这样的配置在.groovy文件中,写法如下:
1 | beans { |
这种配置形式比较等同于xml定义的形式,甚至可以支持xml配置的命名空间,还提供了使用importBeans用来引入xml bean 定义文件。
使用容器
applicationContext 是一个可以维护不同的bean和依赖关系的高级工厂的一种实现。通过T getBean(String name,Class<T> requiredType).你可以创建bean的示例。
ApplictionContext让你能够阅读bean的定义和访问他们。
1 | // create and configure beans |
在 groovy 的配置中,也是非常类似的配置:
1 | ApplicationContext context = new GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy"); |
最灵活的形式是GenericApplicationContext和reader相结合的形式,比如,与XmlBeanDefinitionReader相结合。或者是使用 GroovyBeanDefinitionReader ,如下所示:
1 | GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext(); |
你可以在同一个Application中混合这几种reader delegate,从不同的配置源中获取bean definitions。
你可以使用getbean来实例化你的bean,ApplictionContext提供了其他几种获取bean的方法,但是你的应用代码不应该使用他们,你的代码中不应该使用getBean()方法从而避免依赖Spring APIs,例如,spring 的web模块提供了依赖注入的功能,你可以通过元数据(例如自动装配)来申明特定的bean 的依赖。
bean概览
springIOC容器管理多个bean,这些bean在你将源数据应用到容器时创建。在容器本身内部,这些bean 定义被BeanDefinition这个类管理,它包含了如下的元数据:
- 包限定的类名(a package-qualified calss name):通常,指的是被定义的bean的实际上的实现类。
- bean行为配置元素(bean behavior configuration elements),该状态说明了bean在容器中的行为(scope,lifecycle callbacks,and so forth)
- bean工作所需要的其他关联的beans,这些关联也被叫做合作或者依赖。
- 创建新对象中的其他的配置设置,例如,一个管理连接池的bean中的连接数量
这些元数据转换为构成每个bean定义的一组属性。下表是一些属性的描述:
| Property | Explained In … |
|---|---|
| Class | Instantiating Beans(实例化bean) |
| Name | Naming beans(命名 bean) |
| Scope | Bean Scope(bean的作用域) |
| Constructor arguments | Dependency Injection(依赖注入) |
| Properties | Dependency Injection |
| Autowireing mode | Autowiring Collaborator |
| Lazy initialization mode | lazy initialization beans |
| Initialization method | Initialization callbacks(初始化回调) |
| Destrucition method | Destruction callbacks(注销的回调) |
除了包含如何创建一个特定的bean的信息的bean difinition之外,applicationContext还允许管理那些在外部被创建的对象。这是由ApplicationContext中的BeanFactory通过getBeanFactory()实现的,它返回了BeanFactory的实现类(DefaultListableBeanFactory)。DefaultListableBeanFactory通过registerSingleton()和registerBeanDefinition()提供注册。在一个典型的应用中,常规的bean definition和元数据定义的bean definition会放在一起使用。
tips:
bean的元数据和手动构建的单例需要尽可能早的注册,为了使容器在自动注入阶段和其他的内省阶段正确的推断出他们。在覆盖元数据和已存在的单例在某种程度上是被支持的,在运行时bean的注册不被正式支持,并可能导致并发问题,导致bean容器出现不一致的状态。
Bean的命名
每个bean都有一个或多个标识符。这些标识符在容器中必须是独一无二的。一个bean通常只有一个标识符,假如需要多个,多出来的可以被认为是别名。
在基于XML配置中,可以看到id属性,name属性,或者两者都指定的bean的标识符,id指定的是精确唯一的一个ID, 通常,这些名字都是字母数字(’myBean’, ‘someService’等等) 如果你想要为一个bean引入其他的别名,你可以在元素【name】中指定他们,用逗号【,】,分号【;】或者空白符来分别他们。
历史上,spring 3.1之前的版本,元素【id】被定义成 xsd:ID 类型,限制了可能的字符;从3.1版本开始,它就被定义成了xsd:string类型。尽管不再由XML解析器保证其一致性,容器仍然强制保持其一致性。
name 和 id 对于bean来说不是必须的,如果你没有指明name或者id,容器会自动创建一个name,如果你想通过name来引用bean,通过ref元素或者Service Locator查找,你就必须为他提供一个name。
不提供名称的原因与使用InnerBean和自动装配合作者有关。[存疑]
bean的命名约定:
这个约定是一个标准的java在属性命名上的约定,beanname必须以小写字母开头,驼峰式的一个结构。bean命名可以让你的配置更好的被阅读和理解,另外,如果你使用AOP,可以更方便通过name来应用通知一组bean。
tips:
当组件扫描classpath时,spring为没有命名的组件生成beanname,通过以下的规则:本质上就是将简单类名(不包含包名)的第一个字符转为小写,然而,在一些特殊情况,如果类名的第一个字母和第二个字母都是大写,那么原始的外壳得到保留,会使用通过Introspector.decapitalize规则来创建name
Bean定义之外的别名
在bean定义本身中,对一个bean通过组合使用最多的id的名称和任意数量的name的名称,来构成不止一个bean的名称。这些名称可以看做是同一个bean的等效别名,在某些情况下很实用,例如通过使用特定于该组件本身的Bean名称,让应用程序中的每个组件都引用一个公共依赖项。
指定实际定义的bean的所有别名是不够的,然而,在一些时候,会引入一个在别处定义的bean的别名。在一个配置被分割到各个子系统的大型系统中会经常看到这种情况。各个子系统都可以通过xml配置元数据,拥有自己的对象定义集合,你可以使用<alias>标签去表示他们,下面是一个例子
1 | <alias name="fromName" alias="toName"/> |
在这个例子中,一个叫fromname的bean,通过这个别名定义后,转换为了toName.
又例如,这个子系统A的配置的元数据想要通过subSystemA-datasource关联上一个数据源,子系统B想要通过subSystemB-dataSource 关联一个数据源。当主系统使用了这些子系统后,主系统想要通过myApp-DataSource来引用这个数据源,如果想要这三个名称使用同一个数据源对象的时候,你可以通过以下的配置来完成
1 | <alias name="myApp-dataSource" alias="subsystemA-dataSource"/> |
现在所有的系统都可以通过唯一的,不与其他定义冲突的(特别是创建了命名空间)的name 引用数据源。他们会引用相同的bean。
tips:
java-configuration(java配置):如果你使用javaconfiguration,这个@bean注解可以提供别名,可以参照@bean注解的详情用法。
实例化bean
bean的定义本质上是为了创建一个或多个对象,当被询问时,容器查看命名bean的创建,并通过bean定义封装的配置元数据来创建一个实际的对象。
如果你使用基于xml的配置元数据,你指明了通过bean标签中的class属性实例化的对象的类型。class属性(在内部实际上是BeanDefinition的class属性)通常是强制性的。你可以通过下面两种方式来使用class属性。
- 通常,在容器本身通过反射性的调用其构造函数直接创建bean的情况下,指定要构造的bean类。等效于java的new操作。
- 要指定包含了static工厂方法用来调用创建对象实际上的class,在不常见的情况下,容器会调用一个static工厂方法来创建一个bean,从调用的static 工厂方法 返回的对象类型可能是相同的class或者是不同的class。
tips:
如果你想要配置static嵌套的bean 定义,你需要使用嵌套类的二元名称(A.B)。例如,如果在com.example包中有一个Something的类,这个类中有一个static嵌套类名为Otherthing,这个嵌套类的bean定义就是 com.example.Something$Otherthing。注意这个$标志,将内部类和外部类分隔。
通过构造器实例化
通过构造方法创建bean时,所有正常的类都被spring使用并且兼容。这些类不需要实现任何特殊的接口或者以特定的方式编写,仅仅需要制定bean的class即可,取决于你用于特定bean的IOC类型,你需要一个默认的空的构造器。
SpringIOC 容器管理你想要的任何实际的class,单不仅仅限于管理javabean。很多Spring用户更喜欢带有一个默认构造器和完整的getter/setter方法的bean。你也可以在你的容器中放下非bean风格的特殊class。例如,你需要使用一个不遵守javaBean规范的旧版的连接池,spring可以管理他,在基于xml风格的配置中,你可以这样设置:
1 | <bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean"/> |
对于构造器使用的机制相关和对象构造之后的对象实例属性的细节部分,参照Injecting Dependencies 这一章节
通过静态工厂方法实例化
定义使用静态工厂方法创建的bean时,请使用class属性指定包含静态工厂方法的类,并使用名为factory-method的属性指定工厂方法本身的名称。您应该能够调用此方法(使用可选参数,如稍后所述)并返回一个活动对象,该对象随后将被视为已通过构造函数创建。这种bean定义的一种用法是在旧版代码中调用静态工厂。
下面bean定义是通过调用工厂方法来指定这个bean的。这个定义没有指定返回的class的类型,这个class包含了一个工厂方法,在这个例子中,createInstance() 方法必须是一个静态方法,一下就是一个具体的示例:
1 | <bean id="clientService" |
以下展示了class在前面创建bean定义是如何运行的:
1 | public class ClientService { |
如果想要获取工厂方法的其他参数和在对象之后设置对象实例属性的机制,需要参照 Dependencies and Configuration in Detail.
通过实例工厂方法实例化
和静态工厂方法类似,实例化一个实例工厂调用的而是已存在、非静态方法的bean来创建bean,要使用此机制,请将class属性保留为空,并在factory-bean属性中,在当前(或父或祖先)容器中指定包含要创建该对象的实例方法的bean的名称。使用factory-method属性设置工厂方法本身的名称。以下示例显示了如何配置此类Bean:
1 | <!-- the factory bean, which contains a method called createInstance() --> |
以下示例显示了相应的类:
1 | public class DefaultServiceLocator { |
一个工厂类可以有多个工厂方法,如下:
1 | <bean id="serviceLocator" class="examples.DefaultServiceLocator"> |
下面配置相应的类:
1 | public class DefaultServiceLocator { |
这种方法表明,工厂Bean本身可以通过依赖项注入(DI)进行管理和配置。
tips:
在spring文档里面,factory bean 指的是 在spring容器中通过实例工厂或者静态工厂方法创建的 bean对象。相比之下, FactoryBean (大写的)指的是具体的FactoryBean对象